January 9, 2018 Web Scraping Python Requests Flipkart Beautiful Soup
How to Scrape a Website using Python, Beautiful Soup and Requests
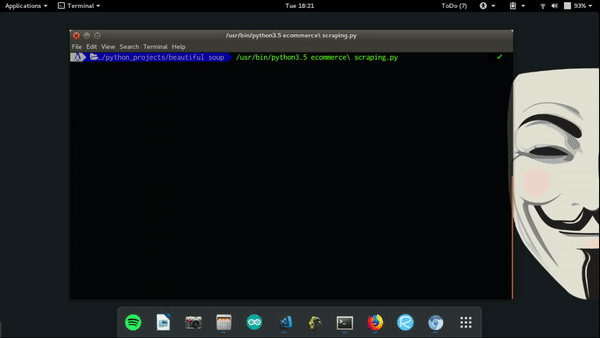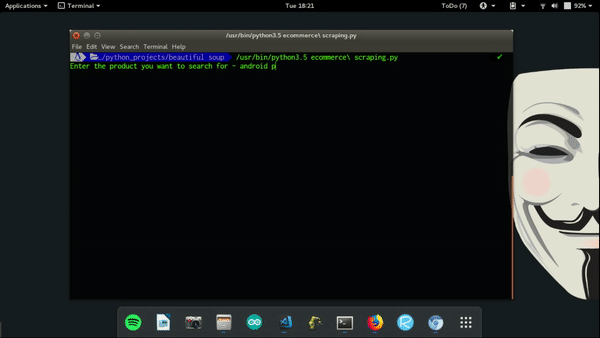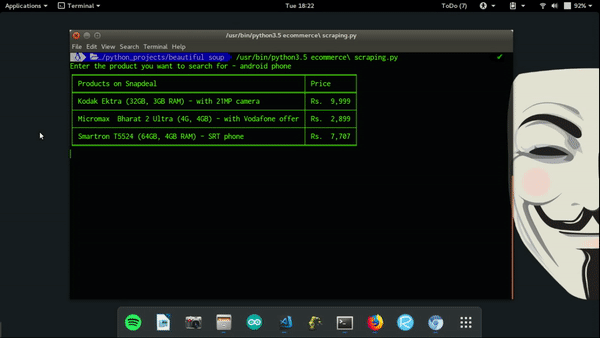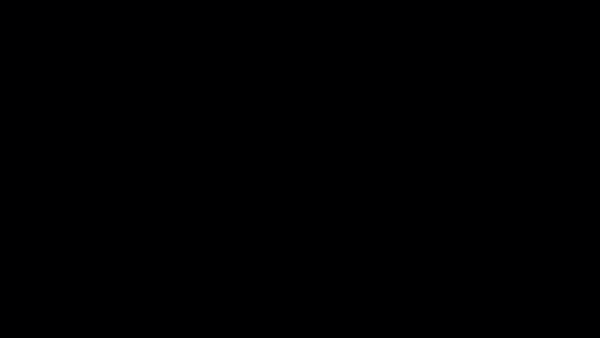
Scraping a website is a technique to pick up data from the website and use it somewhere else. Everything you see on a webpage can be scraped such as text, images, links etc. Web Scraping has many applications, it is used by websites like Policy Bazaar and SmartPrix to compare prizes of products scraped from different e-commerce website, Machine Learning enthusiasts use it to get data for their dataset, search engine companies use it to build website crawlers, it is also used by marketing people to get social media profile, comments and reviews from a website. These are just some usual used cases of web scraping, but you can use it the way you want and build anything you can think of.
Why Web Scraping?
Now you might be thinking “I can just copy paste the required data from the website.” But what if you need to get data from a thousand pages or even more. Copy and paste in that case will take ages. Also we have APIs to serve the purpose. Although APIs are a simple and easy way to get data from a website, it comes with certain restrictions-
- Not all websites provide API service.
- You only get a limited number of API calls.
- In most cases API are only made to provide only limited data.
So why not learn a new skill and build a web scraper according to your own needs. Although web scraping can be done using most of the programming languages but we’ll be using Python due to its simplicity and library support. In this tutorial we’ll be scraping name, rating and price of any product from Flipkart website
Workflow:
These are some steps you need to follow whenever you scrape a webpage:
- Get the URL of the webpage you need to get data from.
- Send a request and get the source code.
- Load the source code into a parser and get the desired data.
- Store the data the way you want.
Setting Up :
Before we start with coding part make sure you have Python3 and pip installed. We will be needing the following python packages:
-
First we need
requeststo send requests to the webpage. Install it using the following command-
pip install requests -
For parsing the source code we’ll use
Beautiful Soupwhich comes withbs4package.
pip install bs4
Let's Code :
Now we are all set up to get the data of any product from Flipkart.
Let’s first import all the libraries we’ll be using-
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
Now we need the URL, for that go to the Flipkart website and search for any product (say pendrive 32GB) and copy the URL. Mine look like this (after simplifying) :https://www.flipkart.com/search?q=pendrive%2032gb
Notice that the query you search for is append to the URL after q= and the spaces are replaced by %20.
So we need to take the input from the user about the product he wants to search for and then append it to the URL . The code will look like this -
#storing the url in url variable
url = "https://www.flipkart.com/search?q="
#taking input form the user and storing it in query variable.
query = input("Enter the product you want to search for: ")
#replacing all spaces with %20 sign.
query = query.replace(" ","%20")
#adding the product name to the url
url = url+query
Now we have our URL ready, let’s send request the the URL and get the Source Code of the website which contains all the data of the webpage. (make sure you have an active internet connection while executing this step)
#sending get request to the url and storing its content in source variable.
source = requests.get(url).content
Once we have have the source code we need to load it into the parser which can parse the content and search for the desired data quickly.
#storing the parsed content in soup variable
soup = BeautifulSoup(source,'lxml')
Now we are ready to extract the data desired data. First we will print the name of all the products:
#finding all the tags which contains the name of products.
names = soup.findAll('a',{'class':'_2cLu-l'})
If you observe the source code you will fond that all the product names are inside a tag which have class _2cLu-l. The findAll function will search for all the a tags which have class _2cLu-l and store them as a list.
To print them just run a loop to traverse all the products stored inside list and print their text:
for item in names:
print(item.text)
For price and rating of products:
rating = soup.findAll("div",{"class":"hGSR34 _2beYZw"})
price = soup.findAll("div",{"class":"_1vC4OE"})
for i,j,k in zip(names,rating,price):
print(i.text,j.text,k.text)
If you want to get the value of an attribute of any tag, like if you want all the links in a website then links are stored in the href attribute of the a tag, this can be done by:
links = soup.findAll("a")
for i in links:
print(i['href'])
In this tutorial we just print the data using loops, in the same way you can store the data also.
You may find the following link helpful if you are storing your data in an Excel Spreadsheet. It contains resources for working in Excel using Python https://www.pyxll.com/blog/tools-for-working-with-excel-and-python/
My Slides on Web Scraping for the Kanpur Python Meetup.
Comment your queries, doubts and suggestion and subscribe to the newsletters.